Your Location:Home > Products > Pharmaceutical > Promethazine hydrochloride

CasNo: 58-33-3
MF: C17H20N2S.HCl
Appearance: white to faint yellow crystalline powder
|
Description |
Phenergan Tablets contain a medicine called promethazine hydrochloride. This belongs to a group of medicines called phenothiazines. Promethazine is a medicine called an antihistamine. It's classed as a drowsy (sedating) antihistamine. Promethazine is used for: short-term sleep problems (insomnia) – including when a cough, cold or itching is keeping you awake at night. allergies, including hay fever and hives (urticaria) feeling and being sick (vomiting) – due to motion sickness or vertigo. |
|
Indications |
PM is used for the treatment of allergic symptoms, often given at night because of its marked sedative effects. Drug hypersensitivity reactions and allergic conditions have also been treated with promethazine especially in emergencies. It can also be used in treating symptoms of asthma, pneumonia, or other lower respiratory tract infections; in fact, inhalation therapy for relieving bronchial spasm is made by quaternary salts of promethazine. PM is sometimes used for its sedative effects and in some countries is marketed for this purpose, including the sedation of young children as nasal sleep introducing drug, or it can be used as an anaesthetic premedication to produce sedation, reduce anxiety, or to reduce postoperative nausea and vomiting as dose-controlled transdermal device. The drug is often given in conjunction with an opiate analgesic such as pethidine, particularly in obstetrics. Taken before travelling, promethazine is effective in preventing motion sickness. Vomiting from other causes can be treated with higher or more frequent doses. Combination of histamine H1R and H4R antagonist is used for the treatment of neoplastic disorders, consisting in a cytotoxic agent as an agent to prevent multidrug resistance[9]. It is also used as a contraceptive killing spermin vagina, since promethazine hydrochloride has strong sperm-killing effect, or as an antimutagenic treatment of bacteria by killing bacteria. Bathing preparation, which contains a histamine H1-antagonist, inhibits the decomposition of hyaluronic acid, playing an important role inmoisture and tension of skin to improve roughened or dried skin. This cosmetic can take such a form as gel, cream, spray, cataplasm, lotion, pack, milky lotion, or powder. It can also be a melanogenesis-suppressing agent useful as a skin-beautifying cosmetic, a skin-aging prevention agent, and so forth, by using a phenothiazine compound having remarkable melanogenesis-suppressing effect. Application of PM can be used for treating haemorrhoids with no pain, no side effect, no operation, and no hospitalization, but low cost[10–12]. Promethazine has been used to control extrapyramidal disorders in children caused by metoclopramide and levodopa-induced dyskinesia in patients with Parkinson’s disease. In young children undergoing dental procedures, it has been suggested that promethazine can be used in conjunction with chloral hydrate to produce sedation, as there was observed a lower incidence of nausea than when chloral hydrate was administered alone. In some countries, promethazine is available as a 2% cream without medical prescription for the treatment of allergic skin conditions, insect bites, and burns. |
|
Mode of action |
Promethazine is a phenothiazine antihistamine, antagonizing the central and peripheral effects of histamine mediated by histamine H1 receptors. The drug does not antagonize histamine at H2 receptors. Antihistamines competitively antagonize most of the smooth muscle stimulating actions of histamine on the H1 receptors of the gastrointestinal tract, uterus, large blood vessels, and bronchial muscle. Increased capillary permeability and oedema formation, flare, and pruritus, resulting from actions of histamine onH1 receptors, are also effectively antagonized. Promethazine appears to act by blocking H1 receptor sites, preventing the action of histamine on the cell. Promethazine rapidly crosses the blood brain barrier and it is thought that the sedative effects are due to blockade of H1 receptors in the brain. Promethazine is not used clinically for its antipsychotic properties but in common with other phenothiazines exhibits antidopaminergic properties. The antiemetic effect of promethazine may be due to blockade of dopaminergic receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone(CTZ) of the medulla. Promethazine has strong anticholinergic properties, blocking the responses to acetylcholine that are mediated by muscarinic receptors. These atropine-like actions are responsible for most of the side effects observed in clinical use of the drug. Promethazine also has antimotion sickness properties that may be due to central antimuscarinic action. In concentrations several times higher than those required to antagonize histamine, promethazine exhibits local anaesthetic effects. Promethazine has also been shown to inhibit calmodulin. Authors have suggested that calmodulin inhibition by promethazine could be a mechanism involved in the blockade of histamine secretion at cellular level[14]. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Slowly oxidizes in air, acquiring a blue color. Also turns blue on exposure to moisture. Water soluble. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Promethazine hydrochloride is sensitive to light. In aqueous solution, Promethazine hydrochloride is degraded by heat and light (more rapidly in air or oxygen). Incompatible with alkalis and alkaline solutions such as those of aminophylline, soluble barbiturates and phenytoin sodium. Iron(III) and copper(III) accelerate the degradation . |
|
Fire Hazard |
Flash point data for Promethazine hydrochloride are not available; however, Promethazine hydrochloride is probably combustible. |
|
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments |
Promethazine may be useful in dogs and cats as an antiemetic. Because of its antihistamine actions, it has been tried for treating pruritus in atopic dogs, but its efficacy has been poor. |
|
Drug interactions |
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Analgesics: possibly increased sedative effects. |
|
Dosage forms |
12.5 mg PO q.i.d.; 25 mg PO at bedtime. May contain saccharin. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: The hydrochloride salt of promethazine. |
|
Brand name |
Phenergan (Wyeth). |
InChI:InChI=1/C17H20N2S.ClH/c1-13(18(2)3)12-19-14-8-4-6-10-16(14)20-17-11-7-5-9-15(17)19;/h4-11,13H,12H2,1-3H3;1H/p-1
Compounds, compositions and methods of t...
The adsorption type can be explained by combined ion exchange and physisorption. Thermodynamic parameters of adsorption of Promethazine hydrochloride (PHCl) onto KSF were also evaluated. The surface morphologies of KSF and PHCl loaded KSF were examined using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). FTIR measurements of samples were also conducted.
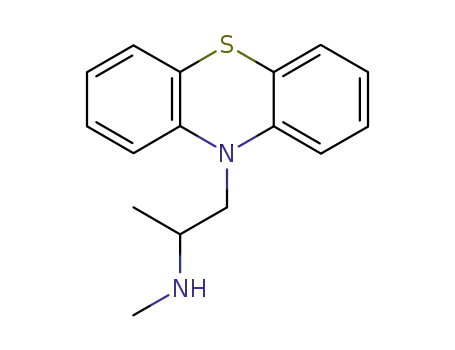
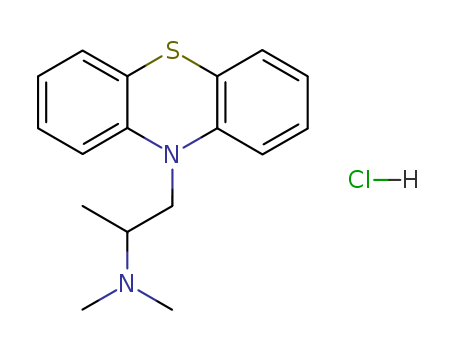
N-Demethylpromethazine
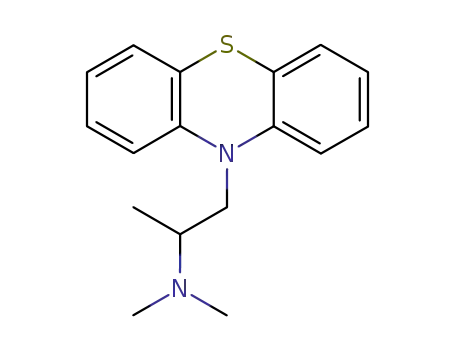
10-[2-(dimethylamino)propyl]phenothiazine
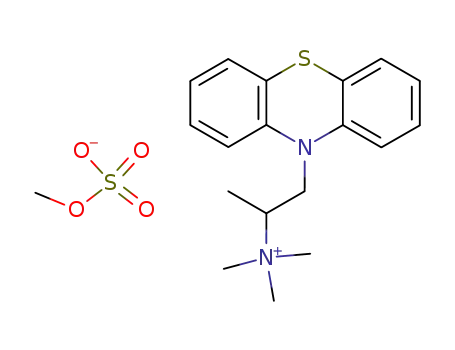
thiazinamium metilsulfate

C23H32N2O3S